Respiratory infections are divided into upper respiratory tract infections and lower respiratory tract infections. Common pathogens in upper respiratory tract infections include influenza viruses, parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, coronaviruses, Ebola virus, coxsackievirus, etc. Lower respiratory tract infections are mainly caused by viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella, and other microorganisms. Upper respiratory tract infections generally have milder symptoms, while lower respiratory tract infections often present as severe, with high mortality rates and poor prognosis.
In the post-pandemic era, various respiratory pathogens are emerging, leading to a surge in demand for respiratory pathogen detection. PCR-based nucleic acid detection technologies have become widely used and recognized. In recent years, well-developed enterprises that seize opportunities and provide hospitals with better solutions are mostly focused on PCR technology, such as ZCHS. However, conventional qPCR technology can only detect a small number of targets, such as triple or sextuple respiratory pathogen detection. Given the diversity and complexity of respiratory pathogen infections, there is a great need for multiplex/ultra-multiplex detection of respiratory pathogens.
In the face of the surging demand, innovative technological solutions for multiplex respiratory nucleic acid detection have become a hot topic in the industry. This article provides a brief analysis from the perspective of technical professionals on the differences between various solutions and how to choose the most suitable one.
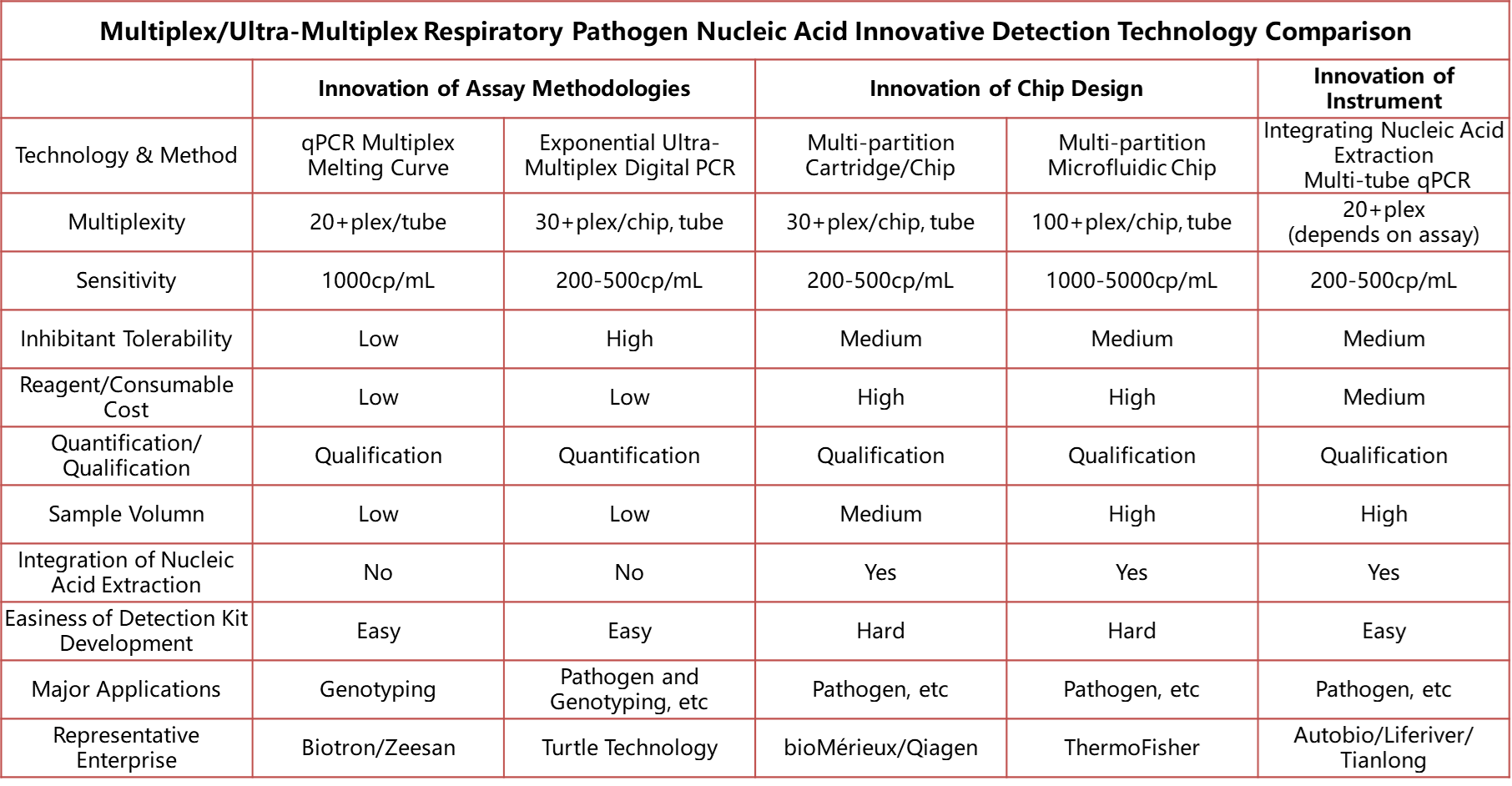
I. Innovation of Assay Methodologies
(1) qPCR Multiplex Melting Curve
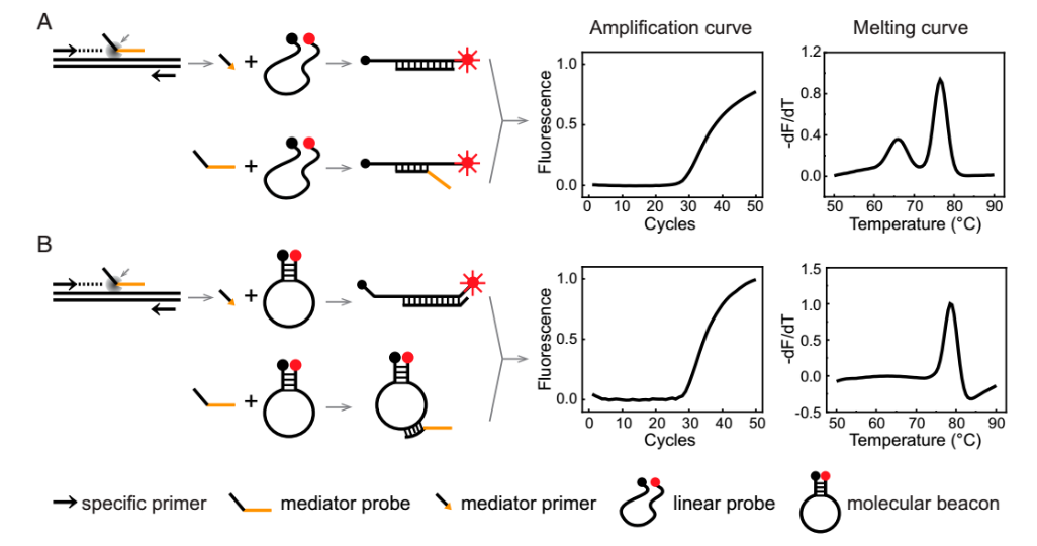
The multiplex melting curve analysis technology is a type of multiplex detection technique implemented on the qPCR platform. This technology utilizes differences in the melting curve peaks to achieve detection and differentiation of multiple targets. It can achieve 20+plex detection in a single tube and has been successfully applied in HPV genotyping and drug resistance detection of tuberculosis (by Biotron/Zeesan). Compared to fluorescent PCR, this technology has significant advantages in multiplexing but exhibits reduced detection sensitivity. Currently, companies like Naturebio have developed single-tube multiplex respiratory pathogen nucleic acid detection products based on this technology[1].
(2) Exponential Ultra-Multiplex Digital PCR Technology
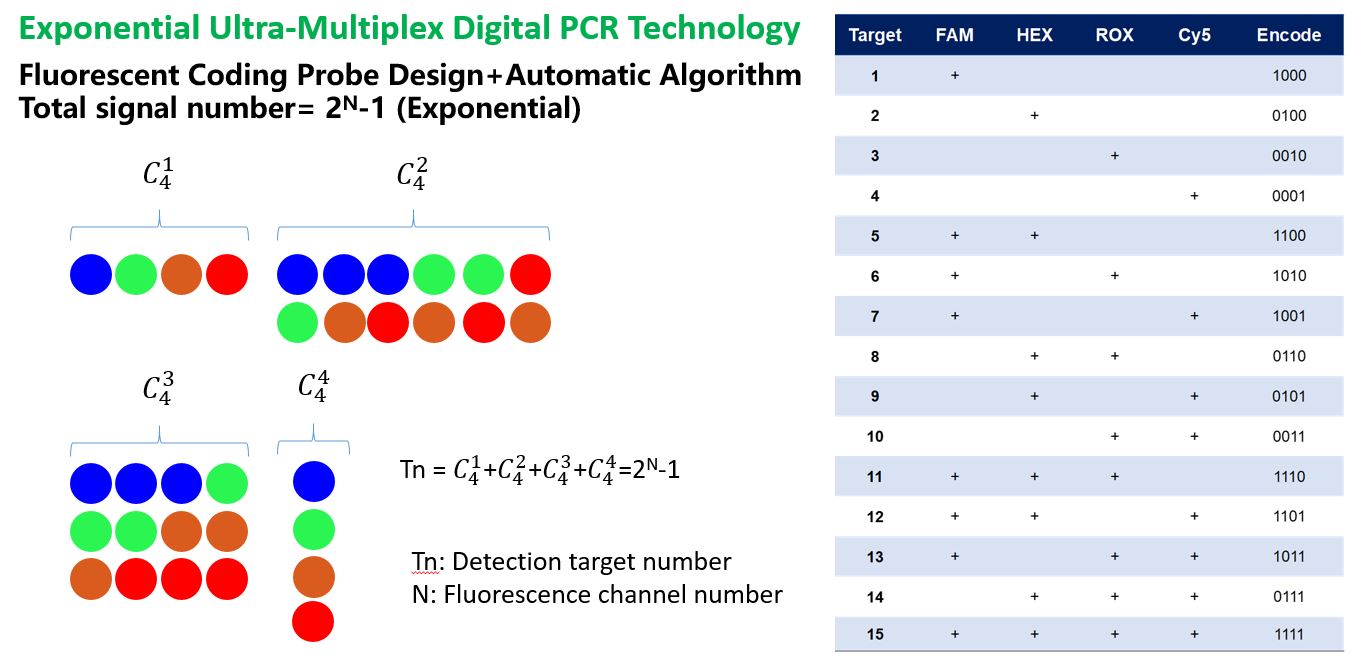
Another innovative method is the Exponential Ultra-Multiplex Digital PCR Technology. This technology, based on digital PCR, utilizes fluorescence encoding and decoding techniques to simultaneously detect 30+ pathogen targets in a single tube. Due to the partitioning principle of digital PCR, it reduces the mutual interference of targets, thus providing significant advantages in detecting complex samples and achieving higher sensitivity. The Exponential Ultra-Multiplex Digital PCR Technology is currently the only method capable of both multiplexing and quantitative detection. It is reported that Turtle Technology has successfully developed single-tube 12-plex and 23-plex respiratory pathogen detection [2]kits using this technology, with a 26-plex blood infection project under development.
II. Innovation of Chip Design
FilmArray® Cartridge/Chip and TaqMan Array Card Microfluidic Chip:
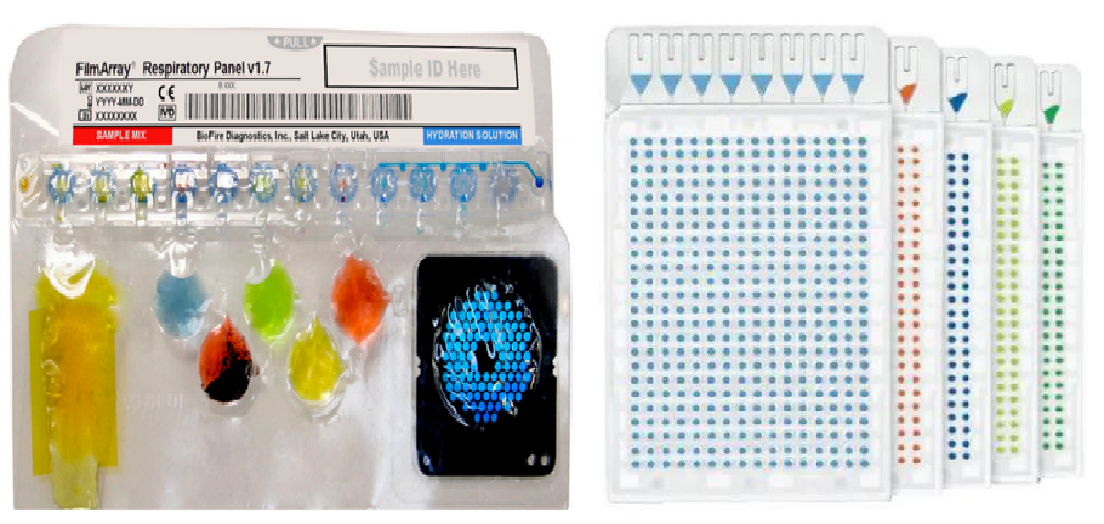

Innovations in cartridge/chip and microfluidic chip technologies have been hot topics in achieving multiplex pathogen detection in recent years. Especially products like FilmArray® from BioFire® Diagnostics, which represent this trend, have become benchmarks in the field of respiratory tract detection, leading to industry-wide emulation. Through automated cartridge packaging, nucleic acid extraction and detection are integrated, making the operation convenient and flexible. The selling price of domestic respiratory tract products is reportedly around CNY 2000 per test. Similar products include Qiagen's kits packed as little blue box. Thermo Fisher Scientific's TaqMan Array Card[3], which utilizes microfluidic chip technology with 384-well plate partitioning, embeds molecular probes in each microchamber, with approximately 1μL per reaction well, enabling single detection of 100+ pathogens in one assay. However, the smaller reaction volume also reduces the sensitivity of pathogen detection.
III. Innovation of Instrument
Autobio[4] - Fully Automated PCR All-in-One Machine

Domestic molecular diagnostics giants are exploring new paths, and in recent years, compared to innovation in basic technologies, innovation in instrument platforms seems to have become the preferred choice for domestic IVD (In Vitro Diagnostics) enterprises. This approach still employs the methodology of multi-tube systems, based on the improvement of automated equipment, integrating nucleic acid extraction and PCR detection for automated multiple pathogen nucleic acid testing. Such products require nucleic acid extraction operations with the lid open inside the equipment, and special attention should be paid to nucleic acid contamination during development.
Summary and Outlook
Overall, the current innovation based on methodology is still in the early stage of productization. Apart from HPV and tuberculosis typing products based on multiplex melting curve analysis, other detection products are relatively few, mostly being explored by small and medium-sized enterprises. It is worth mentioning that Exponential Ultra-Multiple Digital PCR Technology combines multiple quantitative detection features and is a noteworthy innovative technology for nucleic acid testing.
Although current respiratory pathogen detection mainly adopts qualitative testing schemes, looking ahead, quantitative testing may also become mainstream in the future. It could be an alternative route for small and medium-sized enterprises to achieve breakthroughs. According to CDC expert, with the increasing incidence of multiple infections, quantitative testing technology has great clinical value for the identification of major and minor pathogens and the formulation of treatment plans.
Products based on chip innovation are limited by high prices and relatively closed systems, thus having a limited audience. However, with automation and convenience, there is considerable market potential once cost control is achieved. Currently, there are many domestic players following in the footsteps of bioMérieux and Qiagen, most of which are still in the early stages. It is hoped that domestic companies can grasp the essence of existing products in product development, maintain product performance while reducing prices, and will have broad prospects in the future. The development of such products involves the matching of chips, instruments, and reagents, and product developers should consider this carefully based on their own capabilities.
The innovation of instrument platforms itself has relatively low technological barriers, but under the situation where major players in the IVD industry are entering one after another, there is great competitive pressure for small and medium-sized enterprises. From a technical perspective, potential nucleic acid contamination issues are also worth noting. In addition, it is also advocated that large enterprises should pay more attention to basic technologies while pursuing rapid productization, as the innovation of basic technologies is the future of industry development.
Reference:
[4] 安图生物丨AutoMolec 3000全自动核酸提纯及实时荧光PCR分析系统
About Turtle Technology
Turtle Technology is committed to leading the life sciences and molecular diagnostics into the digital era. Having been approved as the National Demonstration Center for Genetic Testing Technology and obtaining the first Digital PCR Metrological Evaluation Certificate, we have introduced a variety of digital PCR systems. This marks a comprehensive technological innovation across the entire industrial chain, including genetic testing instruments, chip consumables, Ultra-Multiplex technology, and ultra-high specificity polymerase.